Contraception and family planning VI: Progesterone only pills (POP)
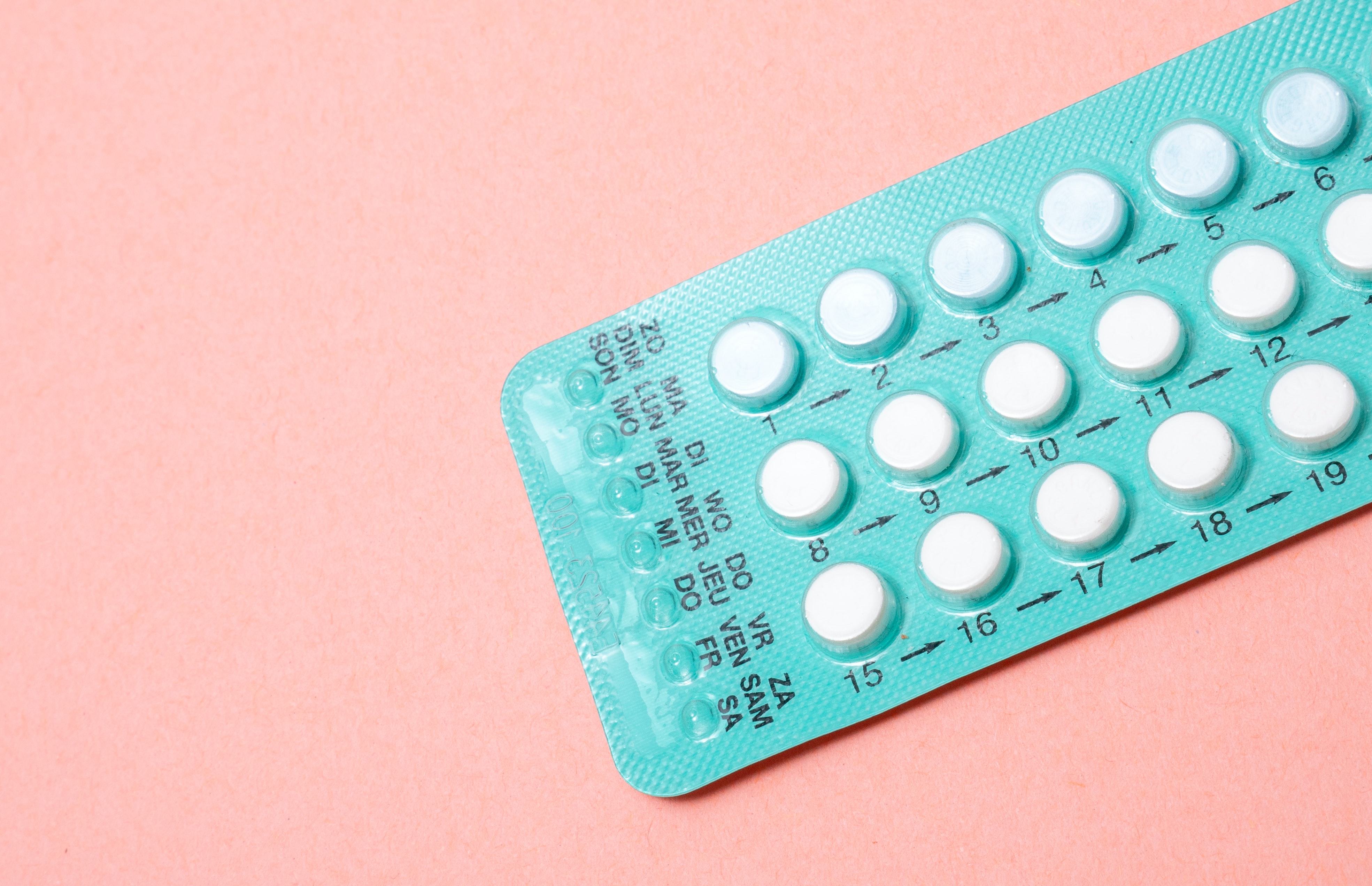
Progesterone-only pills (POP) often called mini pill are contraceptive pills that contains small doses of synthetic progesterone with no estrogen to prevent pregnancy. It works by suppression of ovulation,, thinning of the endometrium and increasing cervical thickness. Examples are traditional POP such as Noriday (Norethisterone) and Microlut (Levenorgesterol) and newer generation of POP such as Cerazette (Desogestrel).
In comparison to combine hormonal contraception pills, POP is safe for patient with migraine and breastfeeding. Its commonly use for older age women with higher risk of estrogen based contraindication such as risk of blood clots and has underlying cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood pressure. POP is contraindicated for patient with breast cancer, has undiagnosed genital bleeding, suspected pregnancy and liver diseases.
It has an effective rate of 91% to prevent pregnancy. It contain 28 pills in a packet and are taken continuously at or around the same time everyday without a pill free period. POP can be started on day 1 to day 5 of the menstrual period without the need for any other added contraceptive method for next 48 hours. If started at anytime (after pregnancy excluded), additional contraception is advised for the next 48 hours.
The traditional POP has only 3 hours window and newer generation POP has 12 hours window. In case of missing pill more than 3 hours late (more than 27 hours from the last pill), the last pill should be taken as soon as remembered, if more than one pill has been missed, only one pill should be taken. The next pill should be taken at the usual time. This may mean that 2 pill are taken in one day. Additional Contraceptive Precautions (condoms or avoidance of sex) are advised for 2 days after restarting the POP. Emergency contraception is indicated if unprotected sexual intercourse occurred after the missed pill and within 48 hours of restarting the POP.
Among side-effects of POP are vaginal spotting and irregular menstrual pattern, acne, breast tenderness, decrease libido, headache and nausea. POP can be stop anytime in the event that patient keen to get pregnant with no delay in return of fertility following the discontinuation.
If you would like to ask more questions about POP or contraception and family planning in general, talk to our doctor for more information.