Animal Bites

Although you may be more worried about bites from wild and stray animals, any animals has the potential to bite including your beloved domestic pets at home. In fact, most common cases of animal bites injury seen at emergency department are caused by domestic animals such as dogs and cats. Children are bitten more often than adults. Management of animal bites depends on the type of animals and degree of injury. In case of venomous animal bites such as snake, patient will require urgent treatment with anti-venom. The most feared complication of an animal bite is rabies. In case of high risk animal bites such as from stray unvaccinated animals, anti-rabies prophylaxis with immune globulin is indicated as bites from animal infected with rabies often result in fatal illness in human
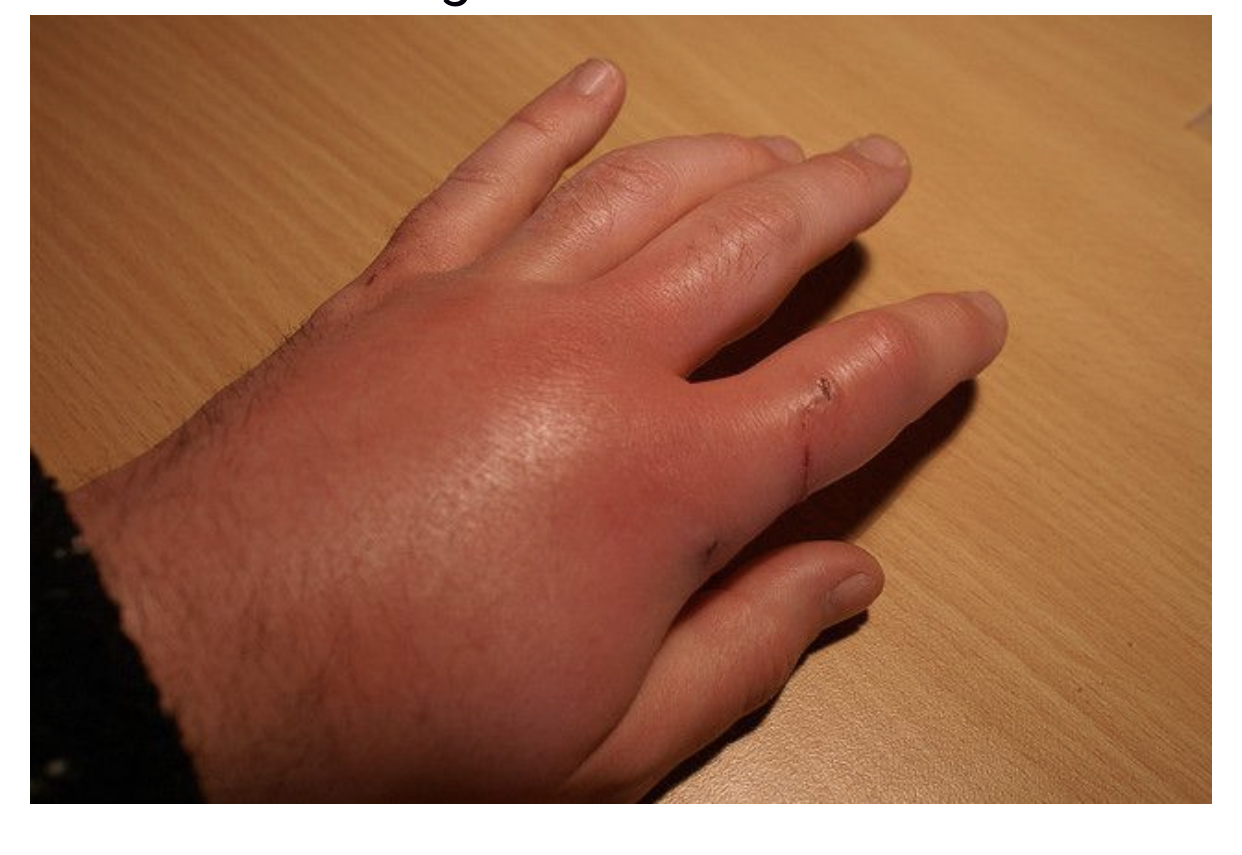
Animal bites can ranges from superficial wound to disfiguring and sometimes fatal wound. Even a minor wound injury can become infected and therefore all animal bites should be evaluated carefully. In case of superficial scratch and bites, treatment can be done in out-patient clinic whereas deeper wound may require surgical intervention in the hospital setting. Wound need to be assessed for extent of injury, involvement of deeper tissue structures such as the tendon, blood vessels and nerve, any compromise in the joint mobility and risk of scarring
Animal bites wound need to be extensively irrigated and cleanse with anti-septic solution immediately before infection set in. If you are at home, quickly and carefully clean the water with soap and large amount of water. If there is active bleeding, take a clean towel or gauze and pressed on the wound to slow or stop the bleeding. After irrigation depending on the degree of tissue injury, stitching may be needed. If there are extensive tissue damage, patient will need to undergo surgery for debridement (removal of damage tissue)
If you have any further questions about animal bites, talk to our doctor more information