Diabetes mellitus type 2

Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the level of sugar (or glucose) in your blood is too high. When you eat foods, your body will produce an enzyme called Insulin, made by an organ called the pancreas to help convert glucose from foods then into the cells to be used for energy. Diabetes mellitus type 2 is characterized by variable degrees of insulin deficiency and resistance, so your body cannot utilize the glucose and it stays inside the bloodstream. Obesity is present in 60–80% of patients with diabetes type 2 and is believed to play a major role in the development of insulin resistance.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is on the rising trend all over the world. This is due to poor dietary choices and a sedentary lifestyle. The prevalence of diabetes in Malaysia is about 20.8% in adults above the age of 30 which is 2.8 million patients! Diabetes is an important risk factor for various complications. This can be divided into several categories:
- Microvascular (small blood vessel) complications
- Nephropathy (damage to the kidney) leading to chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal failure requiring dialysis
- Retinopathy (damage to the eye) leading to cataracts, glaucoma and blindness
- Neuropathy (damage to the nerve) in the hands and legs causing numbness and decrease sensation
2. Macrovascular (large blood vessel) complications
- Brain — leading to stroke
- Heart — leading to heart attack and failure
- To lower limbs — leading to foot ulceration and risk of amputation
3. Increased susceptibility to various infections
4. Sexual dysfunction — causing erectile dysfunctions, decrease libido
The majority of patients with diabetes do not have any symptoms. The most common symptoms are lethargy, increase urination, increased thirst, weight loss, and blurring of vision.
Risk factors for getting diabetes include a family history of diabetes, being overweight or obese, sedentary lifestyle, has diagnosis of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, history of diabetes during pregnancy, smoker, and being older than 40 years of age
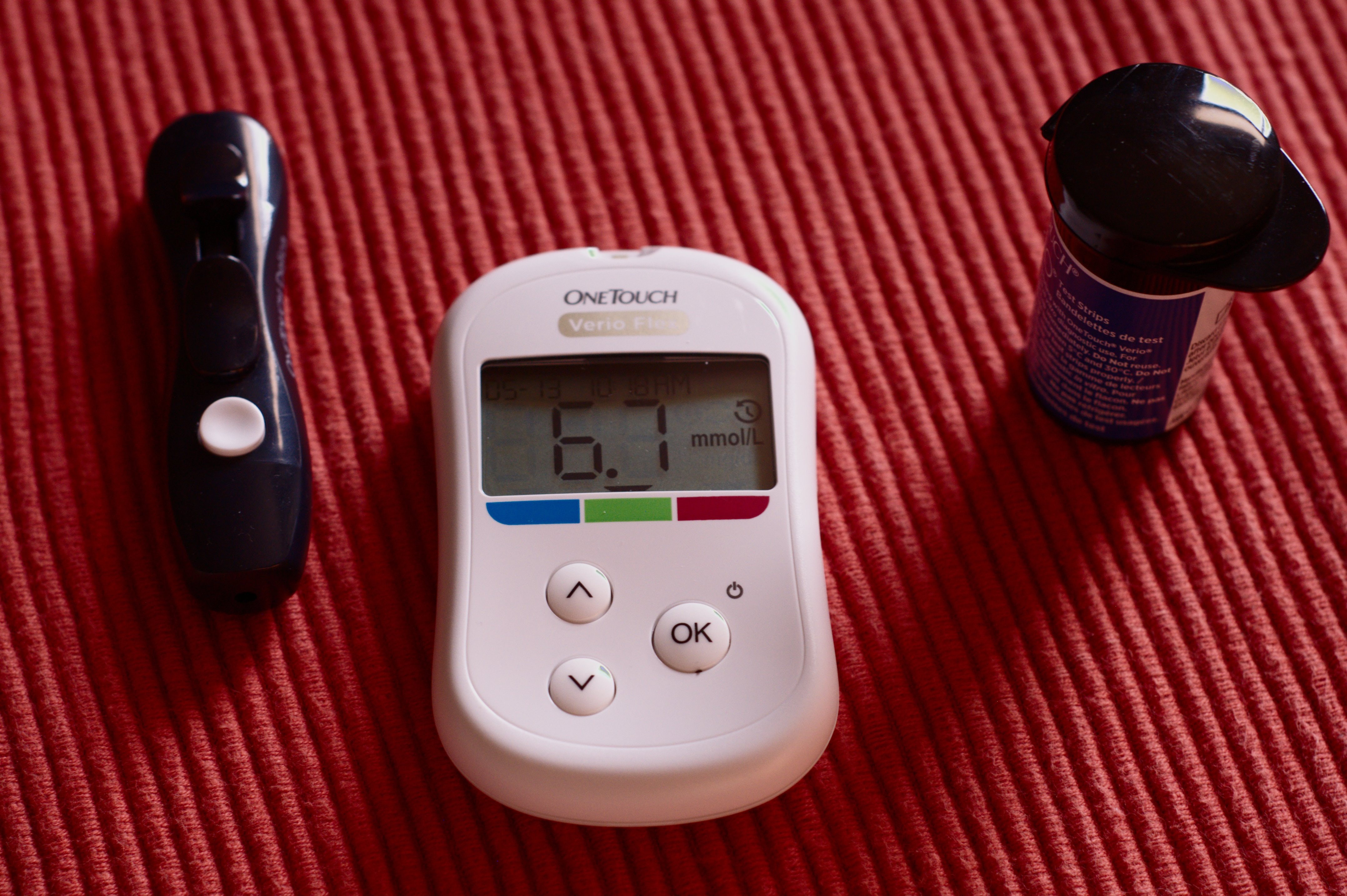
Diagnosis of diabetes can be made by blood testing. Other tests will also be done to screen for other diseases such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol and for end-organ complication such as heart or kidney diseases. Depending on your sugar and HbA1c readings, your doctor will advise you on the treatment needed to help manage your diabetes well. Diabetes cannot be a cure but if managed well, patients can live longer with minimal complications.
This are the strategies that you can do to prevent or manage diabetes:
- Aim for healthy BMI. If you overweight or obese, losing weight can help significantly your diabetes control or prevent you from getting diabetes
- Eat a healthy balanced diet. Choose low glycaemic foods. Completely cut down on sugary drinks and instant coffee. It is also important to avoid foods that are high in saturated fats and excessive salt.
- Regular aerobic and resistance exercise, aim for 5 days a week of exercise and no more than two consecutive days without physical activity. The duration of exercise should be at least 150 minutes/week. Any increase in daily energy expenditure is beneficial e.g. gardening, walking upstairs, washing the car, or mopping the floor
- If you are a smoker, stop smoking. Having diabetes and being a smoker means your risk of complications for heart attack and stroke are much higher.
Managing your diabetes well means regular check- up with your doctor to ensure you are taking your medications correctly. Patient with diabetes on medications can develop symptoms like low blood sugar ('hypoglycaemia') if not taken correctly and have their yearly check of their eye and foot to screen for complications early
If you are concern and have further questions about type 2 diabetes, consult our doctor today for more information.